ECHIDNA

(Short Beaked Spiny Anteater)
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata - Class: Mammalia
- Order: Monotremata
- Family: Tachyglossidae
- Genus/Species:Tachyglossus aculeatus
|
ECHIDNA |
CLASSIFICATION
|
CLASSIFICATION GENERAL INFO HABITAT DIET REPRODUCTION
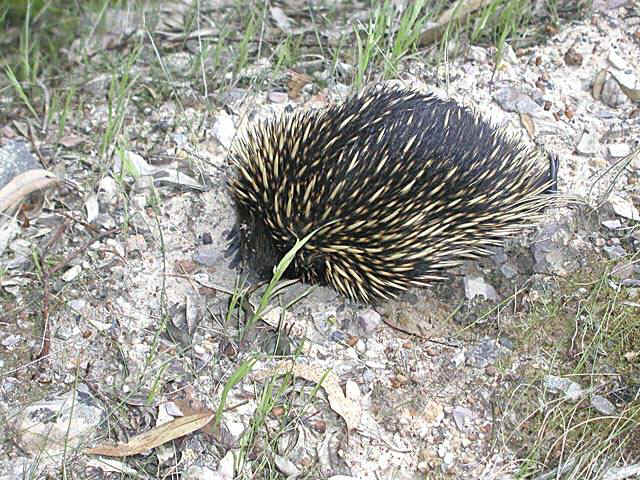
| GENERAL INFO Echidna are MONOTREMES (egg laying mammals). There are only 3 monotremes: the platypus and 2 kinds of echidna. Echidna grow to about 20" in length and their body is covered with large, hollow spines 2-3 inches long. Underneath the spines echidnas have dark brown or black body hair. |
 Echidnas live alone most of the year except during breeding season! |
SPECIAL
FEATURES: Males have a hollow spur on their hind feet, but it is NOT POISONOUS like in the platypus. Echidna milk is
PINK
due |
There are 2 kinds of Echidna. DID
YOU KNOW? WIERD-
In Greek Mythology ECHIDNA |
| DIET Tachyglassus means "fast tongue" and they live up to their name. Echidna eat mainly ants and termites. They use their large claws to open up ant or termite nests, then gobble up the insects with their "sticky" fast tongue. They will also eat worms and grubs and larvae of other kinds of invertebrates. They have NO TEETH and crush their food between hard pads in their mouths. |
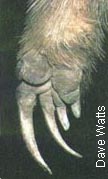 |
 |
REPRODUCTION The breeding season for Echidnas is the end of June to September. Two weeks after mating the female lays ONE EGG with a LEATHERY SHELL from her cloaca into a POUCH on the front of her body. The baby has an egg tooth, to help it break out of the egg when it is ready. When it hatches a baby echidna weighs about 1/8 the weight of a dime! The egg hatches after 10 days
and the baby stays in the pouch, for about 55 days drinking milk, Once they are out of the pouch
they stay in a hollow or cave and the mother comes to feed it. |
 |
HABITAT Echidnas are found all over Australia. They can live in a wide variety of places including: deserts, forests, and highlands... wherever there are ants and termites. They don't stay in a nest or den unless the female is nursing young. They simply find shelter wherever they are: under rocks, fallen logs, in caves, or under bushes. |
| HUMAN
IMPACT: Echidnas have not been hurt as much by habitat destruction as other animals are because echidnas can live anywhere there are ants. However, one problem with interacting with humans is the tendency for echidnas to become "road kill". They are often hit by cars as they cross roads and highways looking for lunch. |
 |
| BODY SYSTEMS: Like all mammals Echinda have a closed circulatory system and a 4 chamber heart. Echidna have fur and make milk for their babies like other mammals, but they lay eggs.
|
|

Echidnas
were a favorite food of Aboriginal people and early |
DEFENSE: To get away from predators, echidnas will burrow down into the soil so only their spines show. On hard surfaces they will curl into a ball with their spines on the outside. Their natural enemies are: Eagles and Tasmanian devils, which even eat the spines! |
SOURCES
http://www.dpiwe.tas.gov.au/inter.nsf/WebPages/BHAN-5357K5?open
http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/accounts/Tachyglossus/t._aculeatus.html
http://www.hlla.com/catalog/echidna.html
Echidna pictures:
http://home.mira.net/~areadman/echidna.htm
http://www.disordered.org/Travel-AU-VC-W.html
Echidna eggs: http://www.saczoo.com/3_kids/17_eggs/_monotremes.htm
Map: Association of National Tourist Office Representatives of Australasia